Featured Videos
All Videos
Injuries to the feet can occur in sports where overuse and undue stress is put onto ligaments and soft tissue. Plantar Faciitis and Achilles Heal are two examples of common injuries. A personal trainer, athletic therapist and a kinesiologist
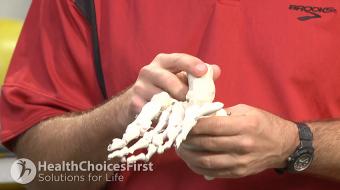
Fractures can occur in the feet because they are exposed to a number of sources of trauma. For example, in a car accident your feet aren’t protected by air bags, so they can easily be fractured. Falling from a height or suffering a twisting injury in sport can also lead to foot fractures.
What is a Stress Fracture?
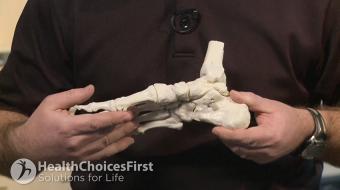
A stress fracture is a small crack or severe bruising in a bone. Stress fractures of the foot are common in athletes, and are usually caused by overuse and repetitive activity. They also occur more commonly in people with osteoporosis, as they have weakened bones. Stress fractures most often affect the:
• Second and third metatarsals in the foot, which get the biggest impact as you push off to walk or run
• Calcaneus, also called the heel
• Fibula, the outer bone of the ankle and lower leg
• Talus, a little bone in the ankle joint
• Navicular, a bone on the top of the midfoot
Foot Fracture Symptoms & Treatments
Symptoms of a foot fracture include:
• Pain that worsens during weight-bearing activity
• Swelling of the foot or outside of the ankle
• Bruising
To diagnose a fractured foot, the physician will do a physical exam and x-rays. As fractures can be difficult to see on an x-ray, your doctor may also recommend a bone scan or a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan.
Depending on the severity of your foot fracture, your doctor might suggest the RICE protocol (rest, ice, compression and elevation), anti-inflammatory medication, a cast and/or crutches. If you require surgery, an orthopaedic surgeon will probably perform a procedure called internal fixation, which involves supporting the bones by inserting pins, screws, and/or plates.
In most cases, a fractured foot will heal in six to eight weeks. It can be challenging to regain range of motion following surgery as there is a lot of stiffness. To regain your range of motion you may need bracing, orthotics and/or physiotherapy to properly heal and return to sport.
Talk to your healthcare provider if you’d like more information on foot fractures.
Visit HealthChoicesFirst.com for more videos and resources on sports health.
Print this Action Plan and check off items that you want to discuss with your healthcare provider
-
A stress fracture is a small crack or severe bruising in a bone. Stress fractures of the foot are common in athletes, and are usually caused by overuse and repetitive activity.
-
Symptoms of a foot fracture include pain that worsens during weight-bearing activity, swelling of the foot or outside of the ankle and bruising.
-
To diagnose a fractured foot, the physician will do a physical exam and x-rays. As fractures can be difficult to see on an x-ray, your doctor may also recommend a bone scan or a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan.
-
Depending on the severity of your foot fracture, your doctor might suggest the RICE protocol (rest, ice, compression and elevation), anti-inflammatory medication, a cast and/or crutches.
-
If you require surgery, an orthopaedic surgeon will probably perform a procedure called internal fixation, which involves supporting the bones by inserting pins, screws, and/or plates.
Adherence:
Adhering to your medications, prescribed exercises or lifestyle changes (such as dietary changes, smoking cessation, reduced alcohol consumption, etc.) is essential to improving health outcomes successfully. Compliance to any prescribed treatment is the number one thing you can do to ensure positive changes and optimal treatment outcomes.